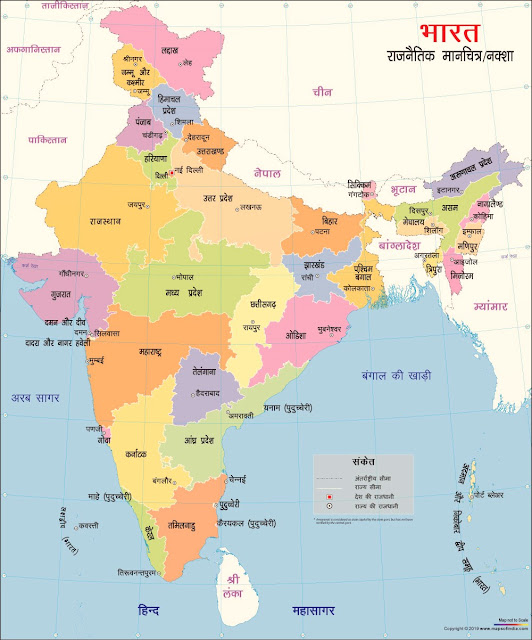
भारतीय भूगोल का परिचय
भारत दक्षिणी एशिया में है। यह दुनिया में दूसरी सबसे बड़ी आबादी है। क्षेत्रफल की दृष्टि से भारत दुनिया का 7 वां सबसे बड़ा देश है। जिसका क्षेत्रफल 3287263 किलोमीटर स्क्वायर है। यह भारतीय प्लेट पर स्थित है, जो इंडो-ऑस्ट्रेलियन प्लेट का उत्तरी भाग है। भारतीय उपमहाद्वीप तीन अलग-अलग जल निकायों से घिरा हुआ है।
भारतीय भूगोल
भारत लगभग 3.28 मिलियन वर्ग किमी के क्षेत्र में फैला है। भारत की मुख्य भूमि 8 ° 4 और 37 ° 6 उत्तरी अक्षांश और 68 ° 7 ′ और 97 ° 25 ° E देशांतर के बीच फैली हुई है। कर्क रेखा 23 ° 30 N भारत को लगभग दो हिस्सों में बांटती है। समुद्र तट की कुल लंबाई 7,517 किलोमीटर है।
भारतीय प्रायद्वीप दक्षिण की ओर जाता है जिसके परिणाम-स्वरूप हिंद महासागर का विभाजन दो जल निकायों में होता है। वे बंगाल की खाड़ी और अरब सागर हैं। भारत में, भू-भागों की बहुत विविधता है जैसे उध्र्वाधर गहरी घाटियाँ, व्यापक मैदान, पठार और तटीय घाट, जैविक सम्पदा, रेगिस्तान और कई द्वीप। भारतीय भूगोल का विभाजन भारतीय भूगोल को दो भागो में बाटा गया है।
- भौतिक भूगोल
- राजनितिक भूगोल
भौतिक भूगोल :- भारत भौगोलिक रूप से समृद्ध और विविध देश है। हमारे देश में वे सभी विशेषताएं हैं जो किसी देश से अपेक्षा करती हैं। इसके पास रेगिस्तान, तटीय क्षेत्र, पहाड़ और पठार हैं। तो हाँ, ये हमारे देश की भौतिक भूगोल विशेषताएं हैं।
इसमें हम भारत के पर्वत, पठार, नदी आदि पर चर्चा करेंगे जो निम्नलिखित है :-
- उत्तर का महान पर्वत
- उत्तरी मैदान
- प्रायद्वीपीय पठार
- तटीय मैदानों
- थार रेगिस्तान
- दीप
उतर का महान पर्वत
उत्तर का प्रमुख पर्वत हिमालय है। 2500KM में फैला यह कश्मीर से अरुणाचल प्रदेश तक फैला हुआ है। हिमालय अपनी अनुदैर्ध्य सीमा में तीन समानांतर श्रेणियों को शामिल करता है। इनमें हिमाद्री या इनर हिमालय या ग्रेटर हिमालय या वृहत हिमालय ,हिमाचल या लघु हिमालय और सिवालिक या बाहरी हिमालय शामिल हैं।
हिमालय की श्रेणियाँ उतर-पशिचम से दक्षिण -पूर्व की दिशा में फैली है। और दार्जलिंग और ये श्रेणियाँ पूर्व -पशिचम दिशा में फैली है जबकि अरुणाचल प्रदेश में ये दक्षिण-पशिचम उतर-पश्चिम ओर मुड़ जाती है। हिमालय प्राकृतिक अवरोधक वल्कि जलवायु ,अपवाह सांस्कृतिक विभाजक भी है।
for more information click below the link ➽
हिमाद्री:- यह सबसे उत्तरी सीमा है। इस श्रेणीकी औसत ऊँचाई 6000 मीटर है। इस श्रेणी की चौड़ाई 160 KM से400KM है। इसमें अधिकांश ऊँची चोटियाँ शामिल हैं जैसे – माउंट एवरेस्ट, नंगा पर्वत, कंचनजंगा। साथ ही, गंगा और यमुनाआदि नदियोंकी उत्पत्ति इसी सीमा से होती है। for more information click below the link ➽
प्रायद्वीपीय पठार उत्तरी मैदान के दक्षिण में स्थित है। इस पठार का आकार एक त्रिभुज के समान कटा -फटा भूखंडहै। जिसका आधार उत्तरी मैदान के दक्षिणी किनारे पर स्थित है और कन्याकुमारी शीर्ष है। उतर -पशिचम में दिल्ली,कटक(अरावली),पूर्व में राजमहल की पहाड़िया ,पशिचम में गिर पहाड़िया और दक्षिण में इलायची(कार्डामम )की पहाड़िया हैइसकी औसत ऊँचाई 600-900 मीटर जितनी है। केरल का अनाईमुडी(2695 मीटर) प्रायद्वीपीय भारत का सर्वोच्च शिखर है,जो अनामलाई पहड़ियो में स्थित है।
इस क्षेत्र में गोल पहाड़ियों और उथली घाटियाँ पाई जाती हैं। गोंडवाना भूमि से निर्मित, यह पृथ्वी की सबसे पुरानी भूमि में से एक है। प्रायद्वीपीय पठार को तीनवर्गों में विभाजित किया जा सकता है
दक्कन का पठार:
यह उत्तर में सतपुड़ा रेंज, पूर्व में पूर्वी घाट और पश्चिम में पश्चिमी घाट से घिरा है। दक्कन के पठार (कावेरी, गोदावरी, कृष्णा) की नदियाँ पश्चिम से पूर्व की ओर बहती हैं। डेक्कन पठार में आंध्र पठार, कर्नाटक पठार और महाराष्ट्र पठार शामिल हैं।
मध्य उच्च भूभाग:-
यह नर्मदा नदी के उत्तर में स्थित है। इस पठार में मालवा का पठार, छोटानागपुर का पठार, मेघालय का पठार, विध्या श्रेणियाँ, सतपुड़ा रेंज और अरावली रेंज शामिल हैं। यहाँ की सबसे ऊँची चोटी गुरु शिखर (1722 M) है। जोअरावली पर है।
उतर-पूर्व पत्थर पठार:-
बास्तव में यह प्रायद्वीपीय पठार का ही भाग है। माना जाताहै की हिमालय की उत्पतिके समय उतर -पूर्व दिशा में कारण ,राजमहल पहाड़ियों और मेघालय के पत्थर के बिच भ्रंश घाटी बने से यह अलग हो गया था। इसमें जनजातियों का आवास है जिसके कारण इन पहाड़ियों का नाम उन जनजातियों के नाम पर ही है। 1. गारो पहाड़ियां 2. खासी पहाड़ियां 3. जयंतिया पहाड़ियां ।
थार रेगिस्तान
भारत का एकमात्र रेगिस्तान थार रेगिस्तान है। इस रेगिस्तान का एक बड़ा हिस्सा राजस्थान में है, लेकिन इसका एक हिस्सा गुजरात, हरियाणा, पंजाब और पाकिस्तान में फैला हुआ है। लूनी एकमात्र नदी है जो इस भूमि से बहती है। रेगिस्तान मेंकेवल 150 मिमी वर्षा होती है। इसे ग्रेट इंडियन डेजर्ट या मारुस्थली के नाम से भी जाना जाता है। इसके अलावा, कुच्छ का महान रण इस रेगिस्तान में आता है। यह माना जाता है की मेसोजोइक काल में यह समुन्द्र था,जिसका प्रमाण आकालमें स्थित काष्ठ जीवाश्म पार्क तथा जैसलमेर के निकट ब्रहासर के समुंद्री निक्षेपों से होती है। जो 18 करोड़ वर्ष आँकी गयी है।
तटीय मैदान:-
तटीय मैदान बंगाल की खाड़ी और अरब सागर के किनारे स्थित हैं। इसे पूर्वी तटीय मैदान और पश्चिमी तटीय मैदान में विभाजित किया गया है।
पूर्वी तटीय मैदान:
यह बंगाल की खाड़ी के किनारे स्थित है और 1100 KM लंबा है। मैदानी क्षेत्र में पश्चिम बंगाल, ओडिशा, आंध्र प्रदेश और तमिलनाडु शामिल हैं। यहाँ, मुख्य नदियाँ महानदी, गोदावरी, कावेरी और कृष्णा हैं,जो डेल्टा विख्यात है
पश्चिमी तटीय मैदान:
यह अरब सागर के किनारे स्थित है और 1400 किलोमीटर लंबा है। मैदान में गुजरात, महाराष्ट्र, कर्नाटक, गोवा और केरल शामिल हैं। यहाँ की मुख्य नदियाँ तापी, नर्मदा और मांडवी,जो डेल्टा का निर्माण नहीं करता हैं। यह एक संकीर्ण पट्टी है। यहाँ पर स्थित प्राकृतिक बंदगाह कांडला मंजगाव तथा कोचीन आदि है। पशिचमी तट को निम्नलिखित भागो में बाटा गया है —
काठियावाड़ तट,कोंकण तट ,मालाबार तट
द्वीप
भारत में द्वीपों के दो समूह हैं:
अंडमान और निकोबार:-
यह बंगाल की खाड़ी में स्थित है और कोलकाता से दक्षिण में 1255 किलोमीटर की दूरी पर स्थित है। द्वीपों के समूहों को उत्तर में अंडमान द्वीप और दक्षिण में निकोबार द्वीप समूह में विभाजित किया गया है।जिनमे 572 द्बीप है। ये द्वीप समुन्दर में जलमग्न पर्वतो का हिस्साहै। साथ ही एक मात्र सक्रिय ज्वालामुखी बैरन आइलैंड निकोबार द्वीप समूह में है।
लक्षद्वीप: –
लक्षद्वीप अरब सागर में स्थित है और केरल के तट से लगभग 200-300 किलोमीटर दूर है। इसमें 36 द्वीप शामिल हैं, पर इनमे 11 पर मनव आवास है। प्रवाल निक्षेपों द्वारा बना है।
राजनितिक भूगोल:-
हिमाचल:-
यह हिमाद्री और सिवालिक श्रेणी के बीच स्थित है। इस श्रेणीकी औसत ऊँचाई 4000 मीटर है। इस श्रेणी की औसत चौड़ाई 60-80 KM है। इसमें महत्वपूर्ण श्रेणियाँ हैं – धौलाधर, पीर पंजाल, महाभारत, शिमला, मसूरी, नैनीताल आदि जैसे प्रसिद्ध हिल स्टेशन इस श्रेणी में स्थित हैं। for more information click below the link ➽
click me
शिवालिक:-
यह सबसे बाहरी श्रेणीहै। जिसकीऔसत ऊँचाई 1000 मीटर है। इस श्रेणीकी औसत चौड़ाई लगभग 10-50 KM है। घाटियाँ जो हिमाचल और सिवालिक के बीच स्थित हैं, जो दुनकहलाती हैं। जैसे:- जम्मू -दुन ,देहरादून ,पठानकोट-दुन आदि। for more information click below the link ➽
उत्तरी मैदान
उत्तरी मैदान महान उत्तरी पर्वत और प्रायद्वीपीय पठार के बीच स्थित है। जिसकी पशिचमसे पूर्व की लम्बाई 3200 किलोमीटर है। जिसकी औसत चौड़ाई 150 से 300 किलो मीटर है। यह तीन प्रमुख नदियों गंगा, सिंधु, ब्रह्मपुत्र और उनकी सहायक नदियों द्वारा बनाई गई है। यह मैदान भारतीय राज्यों पंजाब, उत्तर प्रदेश, बिहार, हरियाणा, पश्चिम बंगाल, असम के क्षेत्र इसके अंतर्गत आतेहै। मैदान बहुत उपजाऊ है क्योंकि यह नदियों के द्वारा निक्षेपसे बनता है। यह भारत में प्रमुख खाद्यान्नों का स्रोत है।
उत्तरी मैदान तीन खंडों में विभाजित है- पंजाब मैदान, गंगा मैदान और ब्रह्मपुत्र मैदान।
पंजाब के मैदान:-
यह सिंधु और इसकी पांच सहायक नदियों – झेलम, चिनाब, रावी, सतलज, और ब्यास नदी द्वारा निर्मित है। और तो और इन्ही नदियों के कारण पंजाब नाम पड़ा है। पंजाब और हरियाणा इस मैदान में आते हैं। इस मैदान का एक बड़ा हिस्सा पाकिस्तान में है।
गंगा के मैदान:-
मैदान का निर्माण गंगा और उसकी सहायक नदियों द्वारा हुआ है। उत्तर प्रदेश, दिल्ली, बिहार, हरियाणा और पश्चिम बंगाल इस मैदान में स्थित हैं। जोग्रेट इंडियन प्लेन का सबसे बड़ा हिस्सा है।
ब्रह्मपुत्र मैदान:-
यह ब्रह्मपुत्र और उसकी सहायक नदियों द्वारा बनाया गया है। इसमैदान को असम के मैदान के रूप में जाना जाता है क्योंकि इसका अधिकांश भाग असम में है।
भौतिक सुविधाओं के आधार पर विभाजन
उत्तरी मैदान भी भौतिक भूगोल सुविधाओं के आधार पर विभाजित है। उत्तर से दक्षिण तक इसे भाबर क्षेत्र, तराई क्षेत्र, जलोढ़मैदान क्षेत्र। जलोढ़ को और दो भाग में बांगर क्षेत्र, कादर क्षेत्र में विभाजित किया गया है।
भाबर क्षेत्र:-
यह हिमालय की तलहटी में स्थित है और लगभग 8-10 किमी चौड़ा पट्टीहै। इस क्षेत्र में ज्यादातर पत्थर ,जोलाशम और कंकड़ हैं। यहां नदियों का बहाव तेज है।
तराई:
तराई भाबर के दक्षिण में स्थित है और 10 -20 किमी चौड़ा है। यह घने जंगल से आच्छादित है और यह क्षेत्र खेती के लिए अच्छा है। और विभिन्न प्रकार के वन्य प्राणियों का आवास भी है।यहां नदी की गति तेज है।
बांगर क्षेत्र:-
यह तराई के दक्षिण में स्थित है और प्रकृति में कम उपजाऊ है। जिसका कारण नदी द्वारा लाये गए बालू रोधिका और बाढ़ है।
कादर क्षेत्र/खादर क्षेत्र:-
कादर बांगर के दक्षिण में स्थित है और यह उपजाऊ भूमि है जो बाढ़ का खतरा है।जिसका समुद्र तल से औसत उचाई 50 से 100 मिटेर है।
प्रायद्वीपीय पठार
Introduction to Indian Geography
India is in South Asia. It is the second-largest population in the world. In terms of area, India is the 7th largest country globally, with an area of 3287263 square kilometers. It is located on the Indian plate, the northern part of the Indo-Australian plate. Three different water bodies surround the Indian subcontinent.
Indian Geography
India is spread over an area of about 3.28 million sq km. The mainland of India stretches between 8 ° 4 and 37 ° 6 north latitude and longitude 68 ° 7 ′ and 97 ° 25 ° E. The Tropic of Cancer 23 ° 30 N divides India into two parts. The total length of the beach is 7,517 kilometers.
The Indian Peninsula moves south, resulting in the Indian Ocean’s division into two bodies of water. They are the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea. There is a lot of diversity of terrains in India, such as deep vertical valleys, vast plains, plateaus, coastal ghats, biological resources, deserts, and many islands. Division of Indian Geography Indian Geography is divided into two parts.
- Physical geography
- Political geography
Physical Geography: – India is a geographically rich, and diverse country. Our country has all the characteristics that a government expects. It has deserts, coastal areas, mountains, and plateaus. So yes, these are the physical geography features of our country.
In this, we will discuss the mountains, plateaus, rivers, etc. of India, which are as follows: –
- The great mountain of the north.
- Northern Plain.
- Peninsular plateau.
- Coastal plains.
- The Thar Desert.
- Deep.
The great mountain of the north
The prominent mountain in the north is the Himalayas. Spread over 2500KM, it stretches from Kashmir to Arunachal Pradesh. The Himalayas include three parallel ranges in its longitudinal range. These include Himadri or Inner Himalayas or Greater Himalayas or Greater Himalayas, Himachal or Small Himalayas, and Siwalik or Outer Himalayas.
The Himalayan ranges extend from north-west to south-east. And Darjeeling and these ranges spread in east-west direction while in Arunachal Pradesh it turns south-west in north-west order. The Himalayas are a natural barrier but also a climatic, runoff cultural divider.
for more information, click below the link
Himadri: – This is the northernmost border. The average elevation of this range is 6000 meters. The width of this range is 160 KM to 400 KM. It includes most of the high peaks like – Mount Everest, Nanga Parbat, Kanchenjunga. At the same time, rivers like Ganga and Yamuna originate from this boundary. for more information, click below the link
Himachal: –
It is located between Himadri and Sivalik range. The average elevation of this range is 4000 meters. The average width of this range is 60-80 KM. It has essential categories – Famous hill stations like Dhauladhar, Pir Panjal, Mahabharat, Shimla, Mussoorie, Nainital, etc. are located. for more information, click below the link
click me
Shivalik: –
This is the outermost category. Its average height is 1000 meters. The average width of this range is about 10-50 KM. The valleys which are located between Himachal and Sivalik are called Dunka. Such as – Jammu-Dun, Dehradun, Pathankot-Dun, etc. for more information, click below the link.
Northern Plain
The Northern Plain is located between the Great Northern Mountains and the Peninsular Plateau. Its length from west to east is 3200 kilometers. Its average width is 150 to 300 km. It is formed by three major rivers Ganga, Indus, Brahmaputra, and their tributaries. This plan falls under Punjab’s Indian states, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Haryana, West Bengal, Assam. The plateau is very fertile as deposits form it by rivers. It is the source of major food grains in India.
The Northern Plain is divided into three sections – Punjab Plain, Ganga Plain, and Brahmaputra Plain.
Plains of Punjab: –
It is formed by the Indus and its five tributaries – Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Sutlej, and Beas. And because of these rivers, Punjab has got its name. Punjab and Haryana come in this field. A large part of this ground is in Pakistan.
Plains of Ganga: –
The plain is formed by the Ganges and its tributaries. Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, Bihar, Haryana, and West Bengal are located in this plain. Jogret is the largest part of the Indian plane.
Brahmaputra Maidan: –
The Brahmaputra and its tributaries form it. This ground is known as the plain of Assam, as most of it is in Assam.
Partitions based on physical features
The Northern Plain is also divided based on physical geography features. From north to south, it is called the Bhabar region, Terai region, plain alluvial region. Alluvial is further divided into the Bangar region, Kadar region.
Bhabar area: –
It is located in the foothills of the Himalayas and has a strip about 8-10 km wide. The area mostly rocks, rock and pebble. The flow of rivers is fast here.
Terai:
Terai is located south of Bhabar and is 10-20 km wide. It is covered with dense forests, and this area is suitable for farming. And it is also home to a variety of wildlife. The speed of the river is fast here.
Bangar area: –
It is located south of the lowlands and is less fertile. The reason is the sand barrier and flood brought by the river.
Kadar Area / Khadar Area: –
Kadar is located south of Bangar and is a fertile land that is prone to floods. It has an average elevation of 50 to 100 meters above sea level.
Peninsular plateau
The peninsular plateau is south of the northern plain.

Bahut achha
Too good
Bahut achha
Good
Its good
Bahut sundar
Too good
Bahut sundar
Good
Good article